
Though naturally produces in the body, the hormone melatonin is often taken as a supplement to aid in sleep. It plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep-wake cycles, making it a popular over-the-counter remedy for sleep disorders.
However, many users and researchers have questioned its potential side effects, particularly its connection to depression. This article seeks to explain the relationship between melatonin and depression, and whether or not melatonin can cause depression.
Depression: A Brief Overview
Depression is a prevalent mental health disorder and a pervasive global issue affecting millions of individuals from all walks of life. It doesn’t discriminate based on age, gender, socioeconomic status, or ethnicity, making it one of the most universally experienced condition.
Types of Depression
Depression can manifest in numerous forms, each with unique characteristics and impacts. Major depression, for instance, is marked by a consistent feeling of despair and disinterest that disrupts daily functioning.
Bipolar disorder, on the other hand, is characterized by fluctuating episodes of mania and depression. Postpartum depression is specific to women who have recently given birth and symptoms include severe mood swings, exhaustion, and anxiety.
Causes and Symptoms of Depression
The causes of depression are multifaceted, involving a complex interplay of genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Some people may be genetically predisposed to depression, while others might develop it due to traumatic experiences or stressful environments.
Recognizing the symptoms of depression is fundamental to early intervention and effective treatment. These symptoms can range from a persistently low mood or feelings of hopelessness to a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed.
Other symptoms can include noticeable changes in sleep patterns, difficulty concentrating and making decisions, persistent headaches, and digestive issues.
Melatonin and Its Role in the Body
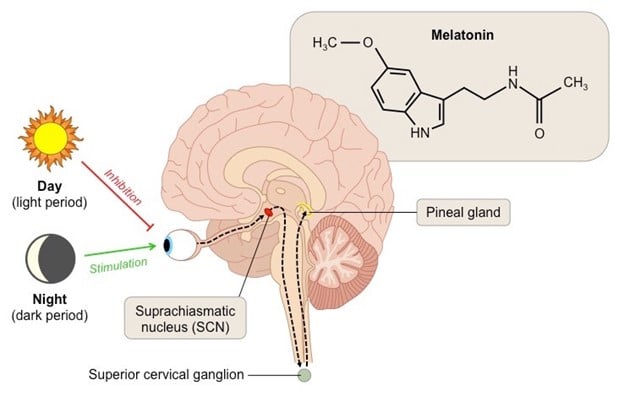
Melatonin, often referred to as the “sleep hormone,” plays a pivotal role in regulating sleep-wake cycles. When produced by the pineal gland in the brain, such production and release of melatonin are influenced by light exposure.
During daylight hours, melatonin production is decreased, signaling the body to stay awake. Conversely, as darkness falls, melatonin production increases, promoting feelings of tiredness and facilitating the onset of sleep.
This process is known as the circadian rhythm, an internal 24-hour clock that runs in the background of your brain and cycles between sleepiness and alertness at regular intervals.
The appropriate balance of melatonin is essential for maintaining normal sleep patterns. Abnormalities in melatonin levels can lead to various sleep disorders, including insomnia and jet lag.
The Influence of Melatonin on Mood Regulation
Melatonin’s influence extends beyond sleep regulation. This hormone is also known to interact with brain receptors responsible for regulating mood states.
Adequate levels of melatonin can contribute to feelings of well-being and happiness, while an imbalance or deficiency may lead to mood disorders such as depression or anxiety.
According to one recent study, the relationship between melatonin and mood is reciprocal: while melatonin can influence mood, emotional states can also affect melatonin levels. For example, high-stress levels can disrupt melatonin production, potentially leading to sleep disruptions and mood changes.
The Relationship Between Melatonin and Depression
Research on the correlation between melatonin and depression is still in its early stages. Current scientific evidence suggests a link between the two, but it is not yet clear if this connection exists because of direct biological effects or due to other factors such as lifestyle changes.
One study found that people taking melatonin supplements experienced a significant decrease in symptoms of depression and an increase in overall well-being. Another study suggested that taking melatonin can help reduce stress levels which may, in turn, alleviate symptoms of depression.
Although the research is not conclusive, it does suggest that melatonin could be helpful for those experiencing mild to moderate depressive symptoms. That said, you should always discuss the potential risks and benefits of melatonin supplements with your doctor before taking them.
The Effect of Melatonin Supplements
Melatonin supplements are often used to alleviate sleep disorders, such as insomnia or disruptions caused by shift work or jet lag. These supplements aim to reestablish a balanced sleep-wake cycle by boosting the body’s melatonin levels.
However, their impact on mood disorders is still a topic of ongoing research. A recent publication on Healthline suggests that melatonin supplements might exacerbate symptoms of depression in individuals already prone to the disorder, possibly due to an overcorrection of melatonin levels or sensitivity to changes in circadian rhythms.
Others argue that melatonin’s sleep-enhancing effects outweigh this potential risk, as adequate sleep is vital for maintaining mental health. Nevertheless, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any regimen of melatonin supplements, particularly for those with diagnosed mood disorders. Personalized advice can ensure the safe and effective use of these supplements.
Long-Term Effects of Melatonin Supplements
Long-term use of melatonin supplements may lead to depression, especially in individuals with mood disorders. Over time, the body might become dependent on supplements, potentially causing a decrease in natural melatonin production.
Other side effects can include daytime sleepiness, dizziness, and irritability, which could adversely impact mood. Some people may experience paradoxical effects, such as increased insomnia and anxiety, contributing further to depressive symptoms.
Finally, prolonged usage without medical guidance might mask underlying health issues causing sleep disruptions, indirectly influencing mood stability.
So, Can Melatonin Cause Depression?
While melatonin supplements are widely used for sleep regulation, their potential impact on mood and mental health shouldn’t be overlooked. Particularly, individuals with pre-existing mood disorders or a propensity towards depression should exercise caution.
There is a plausible link between the long-term use of these supplements and an increased risk of depressive symptoms. Furthermore, they can cause a range of side effects, including daytime fatigue, dizziness, irritability, exacerbated insomnia and anxiety.
Understanding the potential risks and benefits can help you make an informed decision about your health. Contact a mental health professional to discuss whether melatonin supplements are the right choice for you.
Depression Treatment at My TMS
At My TMS, we understand the complexities of depression and the various factors that can contribute to its development. In this blog, we’ve explored the potential link between melatonin and depression, shedding light on the need for cautious consideration when using melatonin supplements, especially in individuals with a history of depression or those at risk.
If you or a loved one is struggling with depression and experiencing treatment-resistant depression (TRD), there is hope. We offer FDA-approved Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy, a breakthrough treatment that can provide a ray of light in the darkness of depression.
TMS therapy is a non-invasive, non-medication-based treatment option that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate specific regions of the brain associated with mood regulation. It has been proven effective in providing relief for individuals with treatment-resistant depression, offering an alternative for those who have not responded to traditional treatments like antidepressant medications or therapy.


